Top 7 Tips for Choosing Orthopedic Surgical Plates for Your Needs
Choosing the right orthopedic surgical plates is crucial for successful surgeries. These plates support bone healing and alignment. According to recent industry reports, the global orthopedic plates market is projected to reach $3.5 billion by 2027. An increasing emphasis on minimally invasive surgeries drives this growth.
Orthopedic surgical plates vary significantly in materials and designs. Titanium plates, known for their strength and biocompatibility, are popular. However, some surgeons still prefer stainless steel due to its affordability. Each option has its pros and cons, and understanding them is vital.
Selecting the appropriate plate requires examining patient-specific needs. Factors like age, activity level, and bone quality significantly influence this decision. While guidelines exist, many choices lack clear-cut answers. Therefore, reflecting on each patient's unique situation is essential. In summary, prioritizing informed choices in orthopedic surgical plates can lead to better surgical outcomes.

Understanding Orthopedic Surgical Plates: Types and Applications
Orthopedic surgical plates play a critical role in various medical procedures. They support fractured bones and assist in proper alignment during healing. Understanding the types available is essential for making informed decisions. There are plates for different applications such as compression, bridging, and locking. Each type serves a specific purpose, tailored to unique patient needs and injury types.
Choosing the right orthopedic plate means considering factors like bone type and fracture severity. It’s crucial to consult experienced surgeons who understand the nuances of these devices. One tip is to look for plates that offer flexibility in placement. This ensures they can adapt to the patient’s anatomy for a better outcome.
Metal composition is another aspect to weigh. Stainless steel and titanium are common options, but each has its pros and cons. A surgeon might advocate for one over the other based on a patient's specific circumstances. It’s worth remembering that not all plates are compatible with every injury, leading to potential issues down the line. Assessing each aspect thoughtfully is vital for optimal healing.
Top 7 Tips for Choosing Orthopedic Surgical Plates
This chart illustrates the key characteristics to consider when choosing orthopedic surgical plates. Each characteristic is rated on a scale from 1 to 10, providing a visual representation of their importance.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Orthopedic Surgical Plates

When selecting orthopedic surgical plates, certain factors are crucial. Material selection is essential. Most plates are made from stainless steel or titanium. Studies show that titanium plates generally offer better biocompatibility. They are lighter and stronger. However, steel plates are more cost-effective. This balance often depends on individual patient needs and financial considerations.
The design of the plate impacts healing and stability. Anatomical plates are molded to fit specific bone structures. This can enhance stability post-surgery. A report from the Journal of Orthopedics noted that improper plate design could lead to complications in 15% of cases. Surgeons must also assess the fracture type. Some fractures require more rigid fixation, while others benefit from flexible systems.
Finally, surgeon experience plays a significant role. Familiarity with particular plate systems can influence surgical outcomes. A study highlighted that surgeons who regularly use specific plates achieve better results. However, reliance on familiar tools may overlook new advancements in the field. Ongoing education is essential to ensure the best patient outcomes.
Material Choices for Orthopedic Surgical Plates: Pros and Cons
Choosing the right material for orthopedic surgical plates is crucial. Common materials include stainless steel and titanium. Stainless steel is known for its durability, but it can cause inflammation in some patients. Research shows that about 30% of patients experience complications linked to poor material choice.
Titanium is lighter and less likely to corrode. It integrates well with bone and minimizes rejection. However, it is often more expensive than stainless steel. Reports indicate that about 20% of orthopedic surgeries involve materials that are suboptimal for the patient’s body. This has raised concerns about long-term outcomes.
Polymer-based plates are gaining attention. They are biodegradable and reduce the need for a second surgery. Yet, their mechanical properties may not match metal plates. Some orthopedic surgeons worry about their reliability in high-stress scenarios. The choice of material must balance cost, effectiveness, and patient compatibility.
Evaluating Plate Size and Fit for Optimal Patient Outcomes
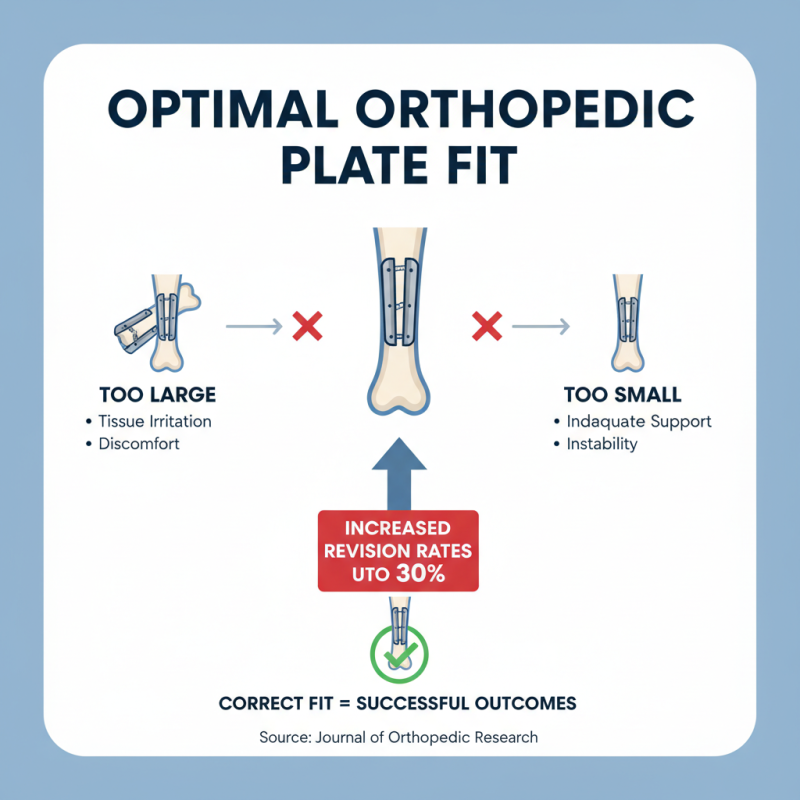
When selecting orthopedic surgical plates, evaluating size and fit is critical for successful outcomes. A plate that is too large can cause tissue irritation. Conversely, plates that are too small may not provide adequate support, leading to complications. According to a study published in the Journal of Orthopedic Research, improper fit can increase revision rates by up to 30%.
Tip: Always verify the dimensions of the plate. Measure both the bone and the plate to ensure compatibility. The anatomical fit of the plate profoundly impacts healing. Research indicates that plates conforming closely to bone contours improve stability and reduce healing time.
In some cases, surgeons may overlook the need for custom or adapted plates. The standard options may not account for unique patient anatomies. Custom plates can enhance surgical precision and improve overall satisfaction. Yet, they require detailed imaging and planning, which can sometimes be overlooked in busy practices.
Tip: Collaborate with a surgical team to evaluate all fitting possibilities. Using 3D imaging technology can aid in pre-surgical planning. It’s essential to prioritize patient-specific needs for optimal recovery outcomes. Factors such as the fracture type, patient age, and activity level matter significantly in this decision-making process.
Consulting with Healthcare Professionals for Best Practices in Plate Selection
When it comes to orthopedic surgical plates, consulting with healthcare professionals is crucial. Surgeons and specialists have the expertise to guide you in selecting the right plate. They understand the nuances of each patient's needs, ensuring a personalized approach. Their recommendations are often based on years of training and experience.
One important tip is to consider your specific injury or condition. Different fractures require different types of plates. For instance, a stable fracture may only need a simple, less invasive plate, while complex fractures might need more robust support. Engaging in detailed discussions with your healthcare provider will help clarify these needs.
Another valuable tip is to inquire about the material composition of the plates. Various materials offer different benefits, such as weight or biocompatibility. Each option has pros and cons. A healthcare professional will provide insight, but always feel free to express your concerns or preferences. Remember, this is your health, and active communication is key.
Top 7 Tips for Choosing Orthopedic Surgical Plates for Your Needs
| Tip | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Consult Experienced Surgeons | Seek advice from orthopedic surgeons with experience in plate selection. | Surgeons can provide insights based on past outcomes. |
| 2. Assess Patient Needs | Evaluate the specific requirements based on the patient's condition. | Different injuries may require different plate specifications. |
| 3. Material Selection | Choose plates made from appropriate materials (e.g., titanium, stainless steel). | Material impacts strength, weight, and biocompatibility. |
| 4. Understand Plate Design | Familiarize yourself with various plate designs and their applications. | Design affects stability and healing process. |
| 5. Consider Manufacturer Reputation | Research the reputation of the manufacturers of orthopedic plates. | Quality and reliability can vary between manufacturers. |
| 6. Review Clinical Guidelines | Stay updated with clinical guidelines regarding surgical plates usage. | Guidelines reflect the latest research and best practices. |
| 7. Evaluate Cost vs. Outcomes | Assess the balance between cost-effectiveness and patient outcomes. | Higher cost may be justified by improved results. |